Search block has been added to create queries by selecting the predefined directives, filters, functions etc. This query builder is an intelligent query processing feature which helps to form queries for new users without prior knowledge of the DQL. The DNIF Query GUI interface lets you search through the data gathered and collated by DNIF. This section introduces you to the various elements and query directives you can use to work with this interface.
How to add a Search Block?
- Hover on the Workbooks icon on the left navigation bar, it will display the folder-wise view of existing workbooks in the tenant (previously known as cluster).
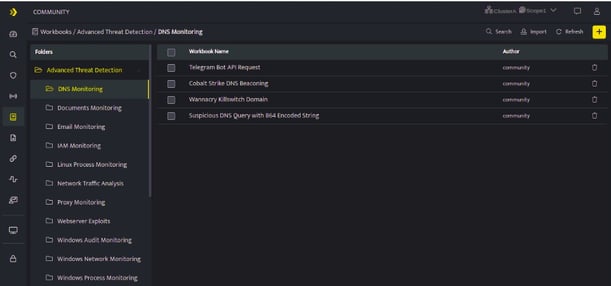
- Click the plus icon at the top right corner , the following Search GUI screen will be displayed.
OR - Click search icon on the left navigation bar, the following screen will be displayed.
The Search Block is the default block, it will be automatically displayed every time you try to create or add a new workbook.
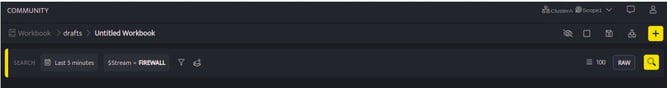
- You can now select streams while building a query using the search block. Select the stream, filters, and set the duration to fetch details
- Select/Enter the required fields to build your query and click Run, a progress bar will be displayed showing that the query is being processed.

- Once the query is successfully processed, the results will be displayed as below.
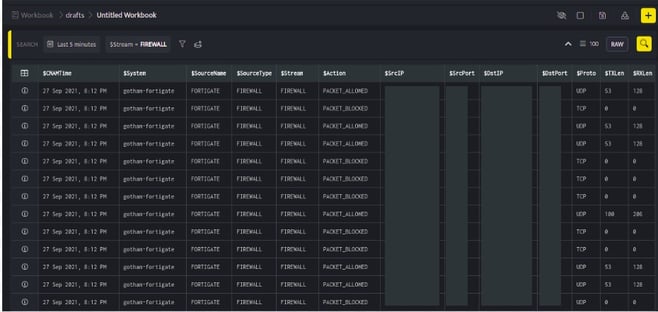
- Click Information icon, to view log details. You can view the log details in JSON and TABLE format.
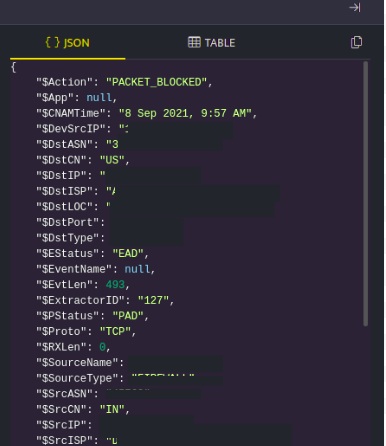
- Click Copy icon, to copy the details to clipboard.
For more details on details on Workbooks, refer Create a Workbook
How to use the search block?
- On adding a search block, the following screen will be displayed.

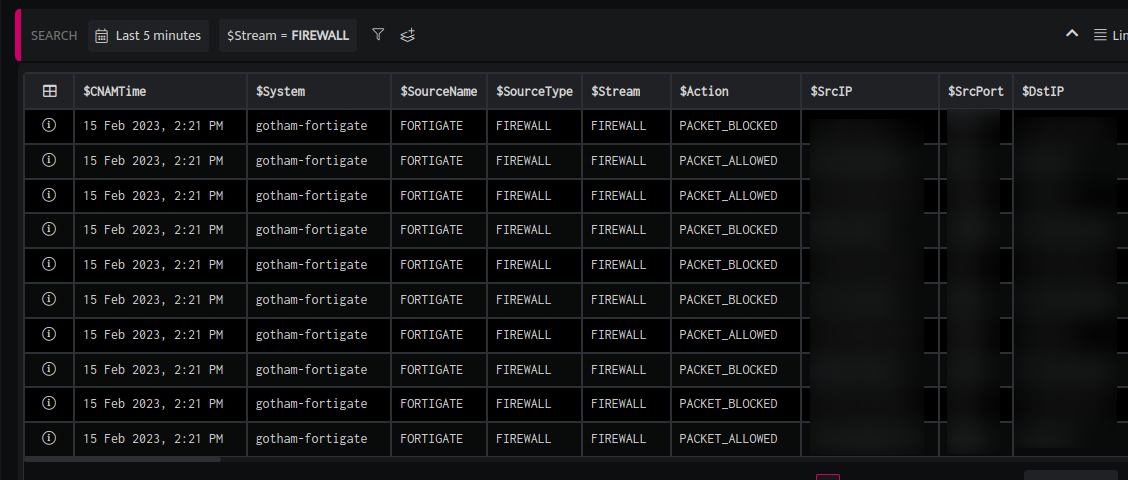
You can customize the query as per your requirement by changing the duration and adding filters.
Wildcard Search using the Search block
You can incorporate additional filters based on specific field values using the wildcard search.
Use wildcards in scenarios where a varied set of end results is possible. The asterisk (`*`) can be used as a wildcard character in conjunction with the search string.
You can use the wildcard operator for the following scenarios:
- You can view the signals with field values ending in a specific pattern by adding the character ‘*’ at the beginning of the search string.
For instance, you can view the list of signals for which the Action is tagged as 'PACKET_BLOCKED' by utilizing the wildcard character as:
$Action = *_BLOCKED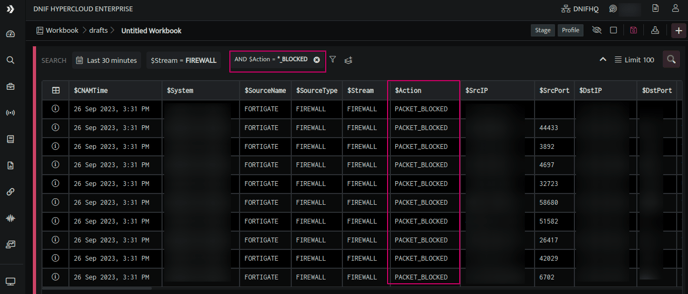
- You can view the signals with field values beginning in a specific pattern by adding the character ‘*’ at the end of the search string.
For instance, you can view the list of signals for which the Encryption status is tagged as 'Not encrypted' by utilizing the wildcard character as:
$Encryption = Not*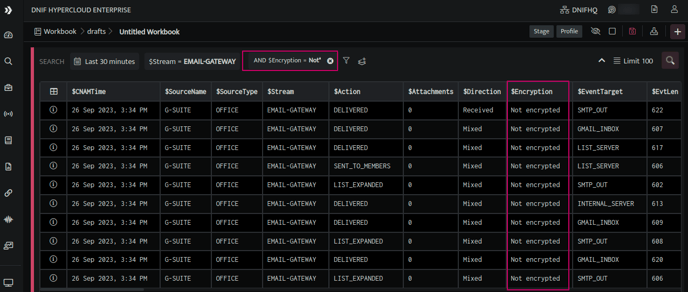
Performance Consideration - It is advisable to use the wildcard-based search judiciously, since it consumes more computational resources and requires more time compared to the standard field search results.
