Code Block also known as a Python Block is used to manipulate the data and generate a new output using python.
- The Python block is a dependent block, so you mandatorily need an input data source from the DQL / Search block.
- The output data from the DQL / Search block will be used as an input to the Python block to manipulate and generate an output.
- It is a restrictive shell, no imports or invocations are allowed. Only standard pythonic functions and operations are allowed.
How to add a Code Block?
- Hover on the Workbooks icon on the left navigation bar, it will display the folder wise view of existing workbooks in the tenant (previously known as cluster).
- Click the plus icon on the Workbook page and select Code Block from the list, the following screen will be displayed.
The python block should be added in the following format:
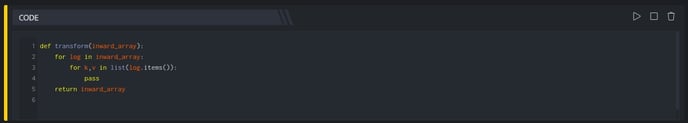
def transform(inward_array):
for log in inward_array:
for k,v in list(log.items()):
if v == None:
del log[k]
return inward_array
| Code | Description |
| def | It is used to define a function and is a mandatory part of the block. For more information refer https://docs.python.org/release/3.0/ |
| Inward Array | Enter the input value from the previous block (DQL) here |
| List | The list that needs to be manipulated as per your requirement. In the above example, all the v= none columns will be deleted from the list. |
| Return inward array | This is also a mandatory field, this would be the result of the manipulations done. It is also mandatory that the return format and the inward format should match. |
- Enter the query and click Run to execute the query, the result dataset will be displayed.
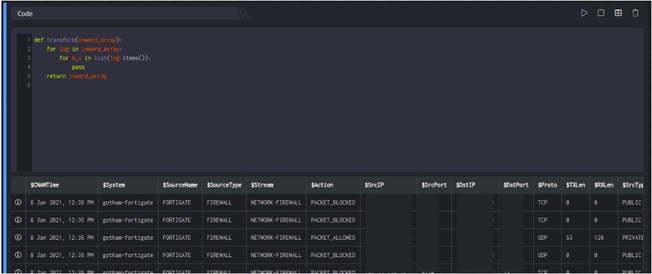
- Click Information icon, to view log details. You can view the log details in JSON and TABLE format.
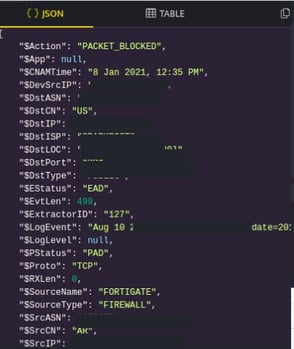
- Click Copy icon, to copy the details to clipboard.
Code Block Functions
| Icons | Functionality |
| Used to execute the query | |
| Used to revoke the executed query. | |
| Used to filter the query result based on your requirement. | |
| Used to delete a block |
For more details on Workbooks refer Create a Workbook.
Usage of json_parse and json_stringify
json_parse is used for parsing data that is received as JSON; it deserializes a JSON string into a JavaScript object. json_stringify on the other hand is used to create a JSON string out of an object or array; it serializes a JavaScript object into a JSON string.
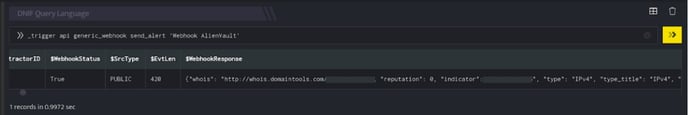
In the below example, a webhook plugin is run, it returns $WebhookResponse in stringified json format.
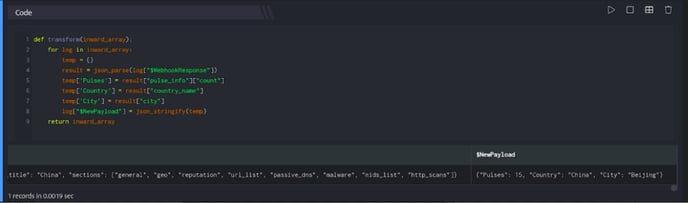
Python code block is used to parse the above mentioned response into a json object and extract the required fields to create a new json object, and json_stringify is used to store it in $NewPayload field
Usage of regexp_extract
Extracts the first string in str that matches the regexp expression and corresponds to the regex group index.
Syntax
regexp_extract(pattern str, string str, group int=0)
Arguments
pattern: A STRING expression to be matched.
string: A STRING expression with a matching pattern.
group: An optional integral number expression greater or equal 0 with default 0.
Returns
The REGEXP_Extract function returns a string value.
The regexp string must be a python regular expression. String literals are unescaped. For example, to match '\abc', a regular expression for regexp can be '^\abc$'. regexp may contain multiple groups. group indicates which regex group to extract. An int of 0 means matching the entire regular expression.
Example
def transform(inward_array):
for log in inward_array:
log["$PacketAction"] = regexp_extract("PACKET_(\w+)", log["$Action"], 1)
return inward_array
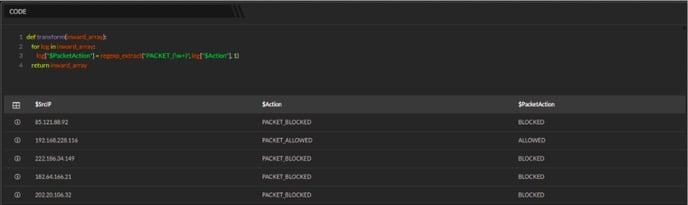
In the above example, the function regexp_extract("PACKET_(\w+) will return all the matching values of PACKET_ from the group viz. PACKET_ALLOWED, PACKET_BLOCKED and the new extracted value is displayed in the $PacketAction column as shown below:
Usage of regexp_match
Returns true if the target value exactly matches the regular expression pattern.
Syntax
regexp_match(pattern str, string str)
Arguments
pattern: A STRING expression to be matched.
string: A STRING expression with a matching pattern.
Returns
The REGEXP_MATCH function returns boolean values.
REGEXP_MATCH attempts to match the entire string contained in pattern str. For example, if pattern str is "ABC123":
REGEXP_MATCH(pattern str, 'A') returns false.
REGEXP_MATCH(pattern str, 'A.*') returns true.
Example
def transform(inward_array):
for log in inward_array:
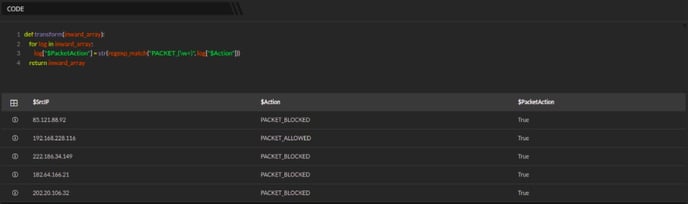
log["$PacketAction"] = str(regexp_match("PACKET_(\w+)", log["$Action"]))
return inward_array
In the above example, the function str(regexp_match("PACKET_(\w+) will return all the matching values of PACKET_ viz. PACKET_ALLOWED, PACKET_BLOCKED and will also return a boolean value corresponding to the string if a substring of the specified string matches the regular expression pattern as shown below: