Magniber is a ransomware program that infects systems by exploiting vulnerabilities in old, outdated software such as Internet Explorer and Adobe Flash. However, it has since evolved to infect other more modern browsers.
Magniber infects machines by posing as Windows 10 cumulative or security updates as bait to trick users into downloading the ransomware payload. You can find these malicious files in downloads on forums, websites offering cracked software and fake websites.
After landing on the victim’s system, Magniber ransomware begins its operation by deleting shadow volume copies. It then encrypts all files stored in each folder except those essential for the operating system's functionality. It uses the RSA+AES encryption scheme when encrypting files in which RSA is 2048 bit, making it difficult to crack. The virus also marks each encrypted file with an additional extension. Some samples of analyzed malware variants used .gtearevf, .vpkrzajx or .nstqjdgxj extension to keep infected files. In other words, the ransomware seems to be using a randomly generated 8 or 9 character string as a new extension for affected data.
At the end of April 2022, Magniber was reported to have disguised itself as a fake Windows 10 update and be a part of a large-scale attack campaign. Recently 360 Security Centre has detected a new attack on the Windows 11 family. The number of attacks reported since May 25, 2022 has increased significantly. Its dissemination package names have been updated to: win10-11_system_upgrade_software.msi, covid.warning.readme.xxxxxxxx.msi, etc.
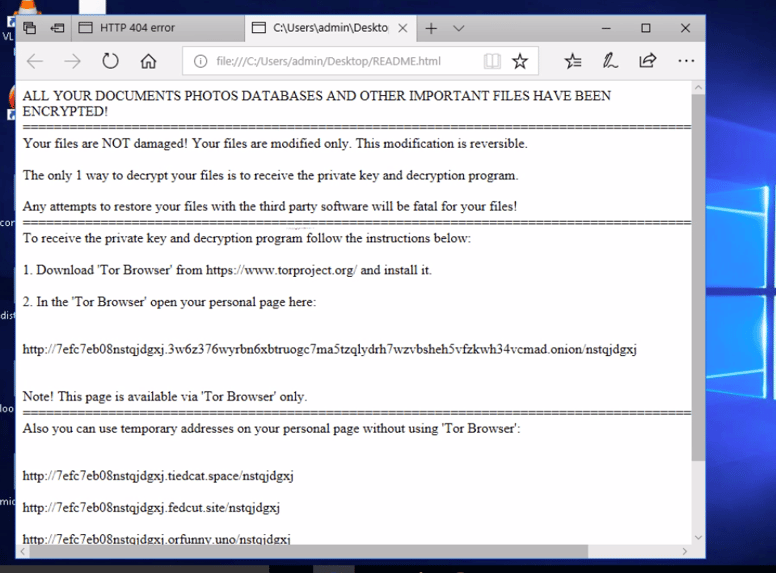
It also creates ransom notes named README.html in each folder that contains instructions on how to access the Magniber Tor payment site to pay a ransom. Each victim is directed to an independent payment page asking them to pay a ransom within five days or the ransom will be doubled.
Analysis and detection of Magniber on DNIF HYPERCLOUD
A user of the organization has executed a windows installer file that is supposed to update the system but it renames all the system files and encrypts it. Post which a ransom attack description prompt is displayed through the browser.
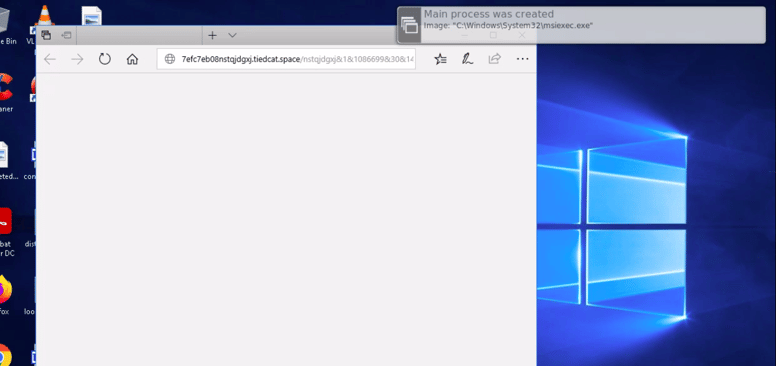
You will be able to see the detection in which the suspect is the hash of the executed file which initiates the ransom attack.
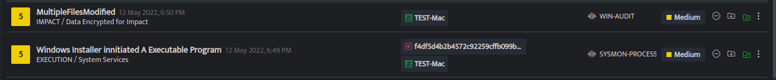
Sysmon Process Creation
We have analyzed the SYSMON-PROCESS logs of the system (TEST-Mac) on which the user has executed a file. You can notice the msiexec process started on the host. Use the lookup panel to get further information and validate your detection.

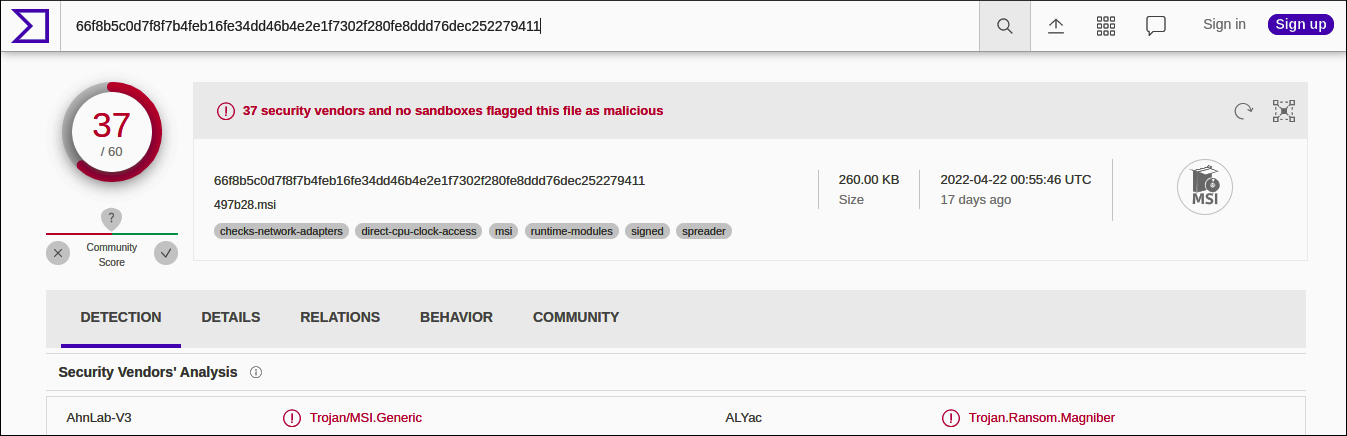
When we click on the suspect i.e hash value, the VirusTotal lookup shows the details about the hash.
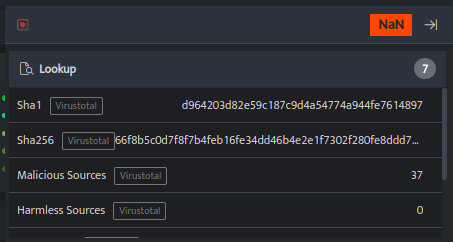
When we further analyze the hash value on Virustotal it shows as Trojan Ransom Magniber.
Connected Signals
To get more insights into the detection DNIF HYPERCLOUD provides a connected signals graph which helps to correlate all the threat detection using common attributes like suspects, hosts, malicious files, path, and name of the malware. These connected signals help the analyst to diagnose the anomalies and compromises on the host in a single cluster view rather than analysing individual signals.
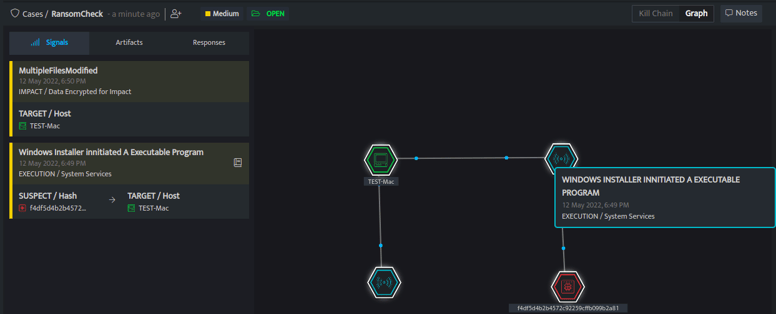
Here, the connected graph shows all the attributes that help to correlate the signals. The first graph shows that a user has executed a Win10.Update-kb8723467.msi file on the system. The suspect marked in red is the hash of the file which was executed and attached. The target is the system on which it was executed. If we re-execute the use case, we can see that a file named C:\\Users\\admin\\AppData\\Local\\Temp\\Win10.Update-kb8723467.msi was executed on the system TEST-Mac by user TEST-USER.

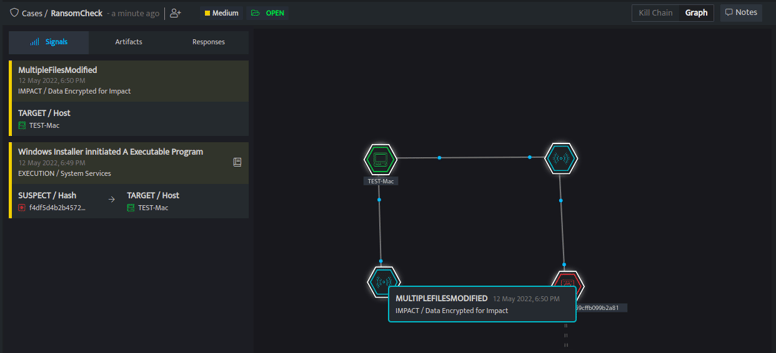
Here you will be able to see the target host where multiple files have been modified from the same system in a short duration.
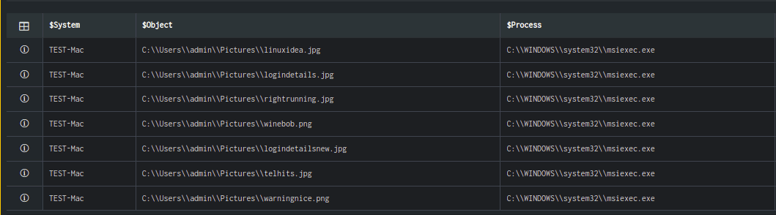
Execute the use case to find the list of the files that were modified. You will notice that all the files are modified by the same process.
Protecting your system from such attacks
Over time the ransomware itself has not changed much, however, its capability to infect multiple versions of Windows operating systems now indicates the continuous work put in by the ransomware group to ensure their malware stays effective. Experts therefore advise users to protect themselves from Magniber by using official websites only to download updates and avoid downloading unknown programs from unknown sources. Read our blog on ransomware attacks and how to avoid them to learn more.
Summary of IOC
.jpg?width=719&name=Magniber%20Table%20(1).jpg)
To know more, Schedule a demo today!


